- Marián Hubinský
- Technologies
- 113575 views
- Tags: Cu, ampacity, current, capacity, table
Current carrying capacity - Ampacity
Frequent question during the development of electronic cabling is "How much current can a 2,5 mm² conductor carry?" or "How thick conductor must be to carry 100 Amps safely?". Answers can be usually found in conductor datasheets where you have to look for Ampacity rating or current carrying capacity...
Frequent question during the development of electronic cabling is "How much current can a 2,5 mm² conductor carry?" or "How thick conductor must be to carry 100 Amps safely?". Answers can be usually found in conductor datasheets where you have to look for Ampacity rating or current carrying capacity.
Current carying capacity of conductors is also known as Ampacity - abbreviation of two words, ampere and capacity.
Choosing the right conductor is a complex task. There are limiting factors, such as air temperature, the ability to dissipate heat and insulation durability. You can find more details in norms IEC 60364-5-52:2009 and BS 7671:2008.
Values below are maximal allowed, it is upmost important to lower them a bit for real-world usage. We are counting with laboratory like, ideal conditions - freestanding, single conductor with PVC insulation (max 70°C), 30°C air temperature, fitting method E according to IEC 60364-5-52.
For any other air temperatures than 30°C, you need to use compensation multiplier of 1.22 for 10°C and 0,50 for air temperature 60°C. This means, at air temperatures of 60°C, it is possible to transfer just half the current.
Just like as applying temperature compensation, we need to apply compensation for having multiple wires next to each other or having multi-core wires, as well as compensating for thermally insulating surroundings which do not allow self-cooling of the wires. During calculations, we also have to count with voltage drop, because this shows us the value of power loss which is then translated to temperature radiation. If we use a multistrand wire lead, most if the time the diameter (multistrand wires have larger core diameter while having the same effective cross section as solid core cables) and parameters for harmonic frequencies changes.
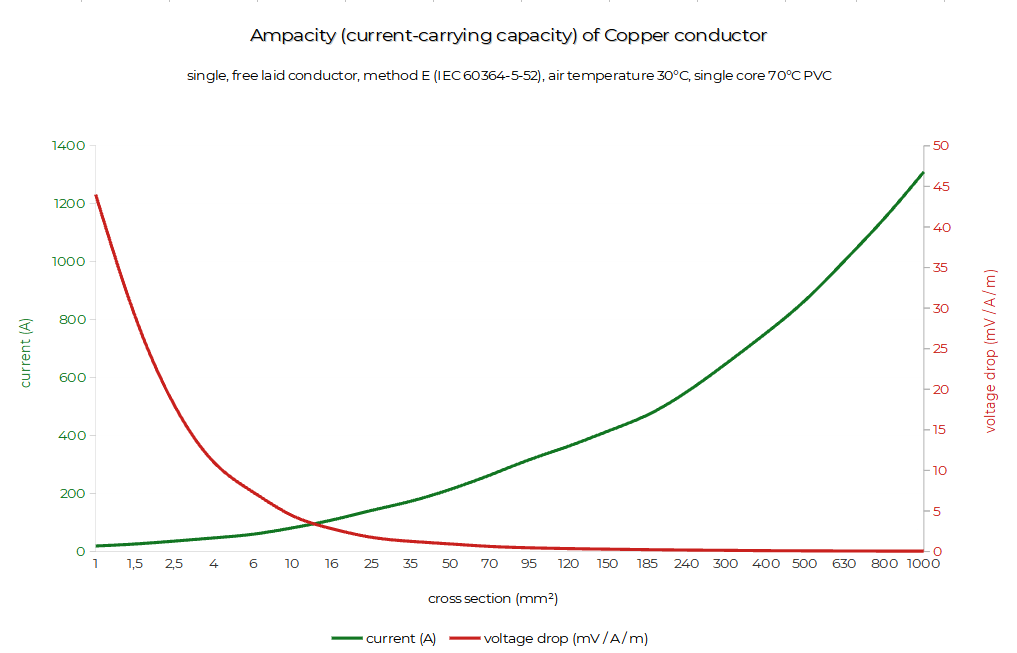
Graph: Current carrying capacity of copper coductors.
Table of maximum theoretical current carrying capacity of copper conductors.
| cross section (mm² Cu) |
max. current (A) |
max. current (A) three conductors |
voltage drop (mV / A / m) |
total voltage drop at max. load (mV / m) |
core diameter (mm) |
| 1 | 19 | 44 | 836 | 1,1 | |
| 1,5 | 26 | 17,5 | 29 | 754 | 1,4 |
| 2,5 | 36 | 24 | 18 | 648 | 1,8 |
| 4 | 47 | 32 | 11 | 517 | 2,3 |
| 6 | 60 | 41 | 7,3 | 438 | 2,8 |
| 10 | 82 | 57 | 4,4 | 361 | 3,6 |
| 16 | 109 | 76 | 2,8 | 305 | 4,5 |
| 25 | 142 | 96 | 1,75 | 249 | 5,6 |
| 35 | 174 | 119 | 1,25 | 218 | 6,7 |
| 50 | 215 | 144 | 0,93 | 200 | 8,0 |
| 70 | 264 | 184 | 0,63 | 166 | 9,4 |
| 95 | 317 | 223 | 0,46 | 146 | 11,0 |
| 120 | 364 | 259 | 0,36 | 131 | 12,4 |
| 150 | 416 | 299 | 0,29 | 121 | 13,8 |
| 185 | 472 | 341 | 0,23 | 109 | 15,3 |
| 240 | 552 | 403 | 0,18 | 99 | 17,5 |
| 300 | 650 | 464 | 0,145 | 94 | 19,5 |
| 400 | 754 | 0,105 | 79 | 22,6 | |
| 500 | 868 | 0,086 | 75 | 25,2 | |
| 630 | 1005 | 0,068 | 68 | 28,3 | |
| 800 | 1150 | 0,053 | 61 | 31,9 | |
| 1000 | 1310 | 0,042 | 55 | 35,7 |
Related products
Delta Elektronika SM15k - séria 15kW zdrojov s rekuperáciou
Fluke 381 - Kliešťový multimeter s iFlex sondou
Marián Hubinský
Elso Philips Service s.r o,
Jilemnického 2/53
91101 Trenčín
Tel.:+421 32 6582410
e-mail: elso@elso.sk